

The normal value is about 6,000mL(4-6 L). Lung capacities It is the maximum volume of air the lungs can accommodate or sum of all volume compartments or volume of air in lungs after maximum inspiration. Restrictive lung diseases cause a decreased lung capacity or volume, so a person's breathing rate often increases to meet their oxygen demands. The volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal expiratory effort.residual air residual capacity. Subsequently, question is, what does it mean to have low lung volumes? In cases of obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchiectasis, COPD, and emphysema, the lungs are unable to expel air properly during exhalation. The amount of air between RV and FRC is the expiratory reserve volume (ERV).

It is the volume remaining in the lungs after expelling as much air from the lungs as possible.
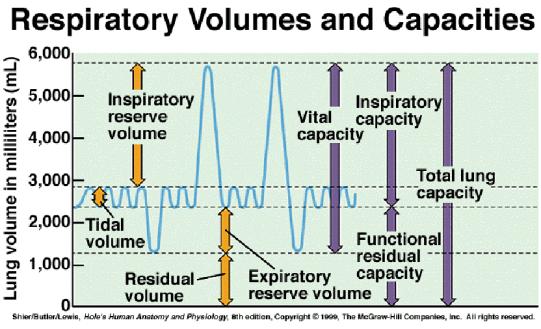
The residual volume (RV) is the amount of air an individual never physiologically expires. In general, however, when reducing the liquid level to between 0.3 and 1.1 mm (residual volume V r 100.00 366.67 µl), the dispensed volume should be checked. Likewise, how do you find the residual volume of a lung? the residual volume V r can be reduced to 100 µl (liquid level 0.3 mm) without problems. In other words, it is the volume of air that cannot be expelled from the lungs.
#Residual volume full#
See /license for the full LOINC copyright and license.Residual volume (RV) is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum forceful expiration. and the Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) Committee. To the extent included herein, the LOINC table and LOINC codes are copyright © 1995-2022, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. LOINC FHIR ® API Example - CodeSystem Request Get Info $lookup?system= LOINC CopyrightĬopyright © 2022 Regenstrief Institute, Inc. Language Variants Get Info zh-CNChinese (China) 体积.残余: 体积型属性: 时间点: 呼吸系统: 定量型: it-ITItalian (Italy) Volume.residuo: Vol: Pt: Apparato respiratorio: Qn: pt-BRPortuguese (Brazil) Volume.residual: Volume: Pt: Sistema Respiratório: Qn: ru-RURussian (Russian Federation) Объём.остаточный: Об: ТчкВрм: Дыхательная система: Колич: es-ARSpanish (Argentina) volumen.residual: volumen: punto en el tiempo: aparato respiratorio: cuantitativo: es-MXSpanish (Mexico) Volumen.residual: Volumen: Punto temporal: Sistema respiratorio: Cuantitativo: Related Names Source: Regenstrief LOINC Fully-Specified Name Component Volume.residual Property Vol Time Pt System Respiratory system Scale Qn Method Additional Names Short Name Residual vol Basic Attributes Class PULM Type Clinical First Released Version 1.0m Last Updated Version 2.48 Member of these Panels LOINCĬontinuity Assessment Record and Evaluation (CARE) tool - Acute CareĬontinuity Assessment Record and Evaluation (CARE) tool - Home Health AdmissionĬontinuity Assessment Record and Evaluation (CARE) tool - InterimĬontinuity Assessment Record and Evaluation (CARE) tool - Post Acute Care (PAC) - AdmissionĬontinuity Assessment Record and Evaluation (CARE) tool - Post Acute Care (PAC) - Discharge However, obstructive disease may be associated with high RV values, which may also be expressed as RV/TLC, which represents RV as a percentage of TLC. Restrictive lung diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, generally lead to a decrease in various lung volumes, while obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma, are associated with preserved total volumes. What is the definition of a large gastric residual volume Edwards and Metheny noted in a review study published in 2000 in MEDSURG Nursing, measurement of Gastric Residual Volume: State of the Science, that the literature had a variety of suggestions for what is considered a high GRV, ranging from 100 to 500 mL. Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after normal exhalation. TLC can be derived as the sum of the vital capacity (VC), the largest volume a patient can exhale after a full inhalation, and residual volume (RV), the volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximum exhalation). Total lung capacity (TLC) is the volume of air in the lungs at maximum inflation. Version 2.72 20146-7 Residual volume Active Part Description


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
